Python-大数据分析之常用库
1. 数据采集与第三方数据接入
1-1. Beautiful Soup
Beautiful Soup 是一个用于解析HTML和XML文档的库,非常适用于网页爬虫和数据抓取。可以提取所需信息,无需手动分析网页源代码,简化了从网页中提取数据的过程,使得数据抽取变得更加容易。
应用场景
- 网络爬虫: 用于从网页中抓取所需数据。
- 数据抽取: 从HTML文档中提取数据并进行分析。
- 数据清洗: 帮助清理和规范不一致的HTML数据。
功能特点
- 解析器灵活性: Beautiful Soup支持多种解析器,如Python的内置解析器(html.parser)、lxml解析器(需要安装lxml库)以及html5lib(需要安装html5lib库)。
- 方便的遍历方法: 可以遍历文档树、搜索特定元素、提取数据。
- 容错能力强: 能够处理“糟糕”的HTML代码,修复标记不完整的标签等问题,让解析过程更加稳定。
- 支持编码转换: 可以自动识别文档编码,或者手动指定编码进行解析。
基本用法
解析器初始化: 通过将HTML文档传递给Beautiful Soup来创建解析器对象。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup# 从文件中读取HTMLwith open("example.html", "r") as file:soup = BeautifulSoup(file, "html.parser")遍历文档树: 可以使用标签名称、类名、id等属性进行文档元素的遍历和搜索。
x# 通过标签名获取元素title = soup.title# 通过类名获取元素important_texts = soup.find_all("p", class_="important")# 通过id获取元素content = soup.find(id="content")提取数据: 可以获取元素的文本内容、属性等信息。
xxxxxxxxxx# 获取文本内容print(title.text)# 获取属性值print(content["href"])修改文档树: 可以添加、删除或修改文档中的标签和内容。
xxxxxxxxxx# 创建新的标签new_tag = soup.new_tag("a", href="http://example.com")new_tag.string = "Link Text"# 在文档中插入新标签content.append(new_tag)
1-2. Requests
需要与网络交互时,Requests库是不可或缺。Requests简化了与目标网站接口的通信,易于使用且功能强大,支持多种HTTP方法和参数设置,能够轻松发送HTTP请求并处理响应。网络爬虫、API调用或是测试网站,Requests都能够让这些任务变得轻而易举。
在企业数据采购中,经常需要与供应商或合作伙伴的API进行数据交换。使用requests库可以轻松实现数据的发送和接收,无论是从外部API获取数据还是向外部API推送数据,都可以通过requests来完成。
Requests库特点
- 简单易用: Requests提供了简洁的API,使得发送HTTP请求变得非常简单。
- 多种HTTP方法支持: 支持GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等HTTP方法。
- 自动解析: 能够自动解析JSON响应和处理URL编码等。
- Session支持: 可以创建持久性会话,保持会话状态,方便维护会话信息。
- SSL证书验证、Cookie支持、重定向等: 提供了多种功能以处理各种HTTP请求和响应情况。
基本用法
- 发送GET请求:通过向外部API发送GET请求来获取数据(获取外部数据源)
xxxxxxxxxx# API数据获取import requestsresponse = requests.get('https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=London&appid=your_api_key')if response.status_code == 200:weather_data = response.json()# 处理数据逻辑# Web数据抓取import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupresponse = requests.get('https://example.com')if response.status_code == 200:soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')# 提取所需数据信息- 发送POST请求:使用POST请求向外部API发送数据(推送数据给外部接口)
xxxxxxxxxximport requestspayload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN'}response = requests.post('https://api.example.com/endpoint', json=payload, headers=headers)if response.status_code == 201:# 处理成功发送数据后的响应- 错误处理与异常情况:
xxxxxxxxxximport requeststry:response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/data')response.raise_for_status() # 如果响应状态码不是200,则会抛出HTTPError异常data = response.json()# 处理数据except requests.HTTPError as http_err:print(f'HTTP error occurred: {http_err}')except Exception as err:print(f'Other error occurred: {err}')- 使用Session保持会话:
xxxxxxxxxxwith requests.Session() as session:session.get('https://example.com/login', auth=('user', 'pass'))# 保持登录状态进行后续请求response = session.get('https://example.com/dashboard')- 处理认证和权限
xxxxxxxxxx# Token认证:使用请求头中的Token进行认证headers = {'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_TOKEN'}# Basic Auth:通过提供用户名和密码进行基本认证。auth = ('username', 'password')response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/data', auth=auth)- 日志记录与监控
xxxxxxxxxximport requestsimport logginglogging.basicConfig(filename='requests.log', level=logging.INFO)try:response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/data')response.raise_for_status()logging.info('Request successful')except requests.HTTPError as http_err:logging.error(f'HTTP error occurred: {http_err}')except Exception as err:logging.error(f'Other error occurred: {err}')
1-3. Beautiful Soup与Requests总结对比
| 特点 | Beautiful Soup | Requests |
|---|---|---|
| 主要功能 | 解析HTML和XML文档,提取数据 | 发送HTTP请求,处理响应 |
| 用途 | 网页解析、数据抽取和处理 | 向服务器发起HTTP请求、处理响应,获取网络数据 |
| 关注重点 | 文档解析、数据提取 | HTTP请求和响应的处理 |
| 主要特点 | - 提供多种解析器 - 方便的API来遍历文档树、搜索元素、提取数据 - 修复HTML不完整标签 | - 提供简洁的API - 支持多种HTTP方法 - 处理认证、Cookie、SSL验证等 |
| 适用场景 | 从网页中提取特定数据、数据清洗、提取链接等 | 发送HTTP请求、获取网页内容、与API进行交互 |
2. 数据分析
2-1. Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook是一个开源的交互式笔记本环境,支持多种编程语言,最常用的是Python。它以网页的形式提供一个交互式界面,允许用户在浏览器中编写和运行代码、展示文本、图像、公式等内容,并保存成为具有可执行代码、可视化结果和解释性文档的笔记本。Jupyter Notebook是数据科学家和研究人员的最爱,无论是在进行数据分析、机器学习建模还是原型设计,Jupyter Notebook都是无可替代的工具。
Jupyter Notebook作为一个灵活、交互式、功能丰富的工具,为数据科学家、教育工作者和开发人员提供了一个方便的平台,可以方便地探索数据、编写文档和演示成果。
主要特点和功能
- 多语言支持: Jupyter支持多种编程语言,如Python、R、Julia等,通过内核系统可以轻松切换语言。
- 交互式运行: 可以分段执行代码,实时查看输出结果,有助于探索数据和算法。
- 富文本展示: 支持Markdown、LaTeX等富文本格式,可以插入文本、图像、公式、超链接等。
- 数据可视化: 可以直接在Notebook中绘制图表、图像等可视化结果,并与代码交互。
- 方便共享: 笔记本可以导出成HTML、PDF、Markdown等格式,方便分享和展示成果。
- 支持扩展: 有丰富的插件和扩展功能,可以增强编辑和运行环境。
用途和应用场景
- 数据分析和可视化: 在数据科学领域广泛应用,用于数据清洗、探索、分析和可视化。
- 教学和学习: 作为教学工具,可以编写教程、示例代码,并直观地展示结果,有助于学习和教学。
- 实验和原型开发: 用于快速原型设计和实验,探索算法、库和新技术。
- 文档编写: 用于编写技术文档、报告和演示文稿,结合代码和解释性文本。
使用方法
- 安装Jupyter Notebook: 通过pip或conda安装Jupyter Notebook。
- 启动Jupyter Notebook: 在命令行中输入
jupyter notebook,会在浏览器中打开Jupyter界面。 - 创建和编辑笔记本: 在界面中新建Notebook文件,选择所需编程语言的内核,开始编写和运行代码。
- 编辑和运行代码: 将代码写入单元格,按下Shift+Enter执行单元格中的代码,并查看输出结果。
- 添加文本和图像: 使用Markdown语法添加文本、标题、图像等丰富的内容。
- 保存和分享: 可以保存笔记本为.ipynb文件,也可以导出成其他格式用于分享。
2-2. NumPy
NumPy是Python中用于科学计算的一个强大的库,主要用于处理数组和矩阵运算。它提供了丰富的功能和高效的数据结构,是许多科学和工程领域中常用的核心库之一。
主要特点和功能
- 多维数组对象: 提供了
ndarray对象,用于表示多维数组,可以进行高效的数值运算。 - 数学函数: 包括线性代数、傅立叶变换、随机数生成等丰富的数学函数和工具。
- 广播功能: 能够处理不同形状的数组,自动执行元素级运算,极大地简化了代码编写。
- 性能优化: NumPy底层使用C语言编写,操作数组的运算速度非常快,是因为它具有优化的算法和数据结构。
- 与其他工具集成: 可以与其他工具(如Pandas、Matplotlib等)良好集成,为数据分析和可视化提供基础支持。
- 多维数组对象: 提供了
用途和应用场景
- 数据处理和分析: 在数据科学领域中,NumPy常用于处理、转换和分析数据,尤其是大量数据的计算。
- 科学计算: 在科学计算、工程领域,例如物理学、生物学、金融学等领域,用于模拟、分析和解决数学问题。
- 机器学习和人工智能: 在机器学习领域,NumPy用于处理和转换数据,作为许多机器学习算法的基础。
- 图像处理: 在图像处理和计算机视觉中,NumPy提供了对图像数据进行处理和操作的功能。
- 基本用法示例
NumPy使用介绍可见另一篇博客文章:https://blog.csdn.net/wt334502157/article/details/128185332
2-3. pandas
Pandas是Python中用于数据处理和分析的强大库,它建立在NumPy的基础上,提供了更高级的数据结构和工具,使得数据操作更加便捷和高效。Pandas通常用于处理结构化数据,比如表格数据、时间序列等,无论是需要进行数据清洗、转换还是统计分析,Pandas都可以帮助您快速达成目标
主要特点和功能
- DataFrame对象: 提供了
DataFrame对象,类似于电子表格或SQL数据库中的表格,用于处理二维数据。 - Series对象: 提供了
Series对象,类似于一维数组或列表,用于处理一维数据。 - 数据对齐和处理: 能够轻松处理缺失数据、重复数据、数据合并、数据对齐等操作。
- 灵活的数据操作: 支持数据的切片、筛选、聚合、分组等操作,操作更简单直观。
- 数据读写: 支持多种数据格式的读写,如CSV、Excel、SQL、JSON等。
- 数据可视化: 集成了Matplotlib等库,能够进行数据可视化和绘图操作。
- DataFrame对象: 提供了
用途和应用场景
- 数据清洗和预处理: 用于处理和清洗数据,包括缺失值处理、数据转换、数据规范化等。
- 数据分析和探索: 在数据科学领域中,用于数据探索、统计分析、建模等。
- 时间序列处理: 用于处理时间序列数据,如金融数据、传感器数据等。
- 数据可视化: 可以配合Matplotlib等库进行数据可视化,绘制图表和图形。
- 基本用法示例
Pandas使用介绍可见另一篇博客文章:https://blog.csdn.net/wt334502157/article/details/128219770
3. 数据展示
3-1. matplotlib
Matplotlib是Python中用于绘制图表和可视化数据的库,是Python中最常用的数据可视化库之一,无论是在制作科学图表、数据可视化还是报告,都具有高度的可定制性,Matplotlib提供了丰富的绘图选项,可以让数据以最吸引人的方式呈现。
主要特点和功能
- 各种图表类型: 支持线图、柱状图、散点图、饼图、直方图、等高线图等多种类型的图表。
- 高度可定制: 用户可以对图表的各种属性进行自定义,包括颜色、线型、标签、标题等。
- 支持多种输出格式: 可以生成图像并保存为多种格式,如PNG、JPG、SVG、PDF等。
- 交互式功能: 结合Jupyter Notebook等环境可以实现交互式图表展示。
- 与Pandas集成: 可以方便地与Pandas等库结合使用,直接绘制DataFrame中的数据。
用途和应用场景
- 数据可视化: 在数据科学和数据分析中广泛应用,用于展示和传达数据分析的结果。
- 科学研究: 在科学研究中用于绘制实验数据、模拟结果和科学图表。
- 工程和统计分析: 用于制作工程图、统计图和报告图表。
- 教学和学习: 作为教学工具,用于制作教程、教材以及演示。
基本用法示例
- 绘制折线图:
xxxxxxxxxximport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]y = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
plt.plot(x, y)plt.xlabel('X Axis')plt.ylabel('Y Axis')plt.title('Line Chart')plt.show()
- 绘制柱状图:
xxxxxxxxxximport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = ['板甲', '锁甲', '皮甲', '布甲']y = [30, 12, 37, 26]
plt.bar(x, y)plt.xlabel('装备类型')plt.ylabel('玩家占比')plt.title('各甲玩家占比')# Windows 设置显示中文plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'plt.show()
- 绘制散点图:
xxxxxxxxxximport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]y = [2, 2, 6, 9, 16]
plt.scatter(x, y)plt.xlabel('X Axis')plt.ylabel('Y Axis')plt.title('Scatter Plot')plt.show()
- 绘制雷达图
xxxxxxxxxximport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 创建figurefig = plt.figure(dpi=120)# 准备好极坐标系的数据# 半径为[0,1]r = np.arange(0, 1, 0.001)theta = 2 * 2*np.pi * r# 极坐标下绘制line, = plt.polar(theta, r, color='#ee8d18', lw=3)plt.show()
4. 机器学习
4-1. seaborn
Seaborn是建立在Matplotlib之上的数据可视化库,专注于创建具有统计意义的各种图表。它提供了简单的高级接口,可以轻松地创建漂亮的统计图表,并且具有更好的默认设置,使得数据可视化变得更加简单和直观。
Seaborn提供了一些Matplotlib不提供或不易实现的高级图表类型,如小提琴图、热图、分布图等,这些图表类型能更好地展示数据的分布、关系和特征;具有更好看的默认主题和调色板,使得图表外观更为美观,无需额外调整,让用户在默认情况下就能得到具有吸引力的图表。
虽然Seaborn更加强大,但并不是取代Matplotlib,而是在Matplotlib的基础上提供了更多的功能和便利性,特别适用于统计分析、数据探索和一些高级的可视化需求。在实际应用中,它们可以结合使用,根据不同的需求选择合适的库来绘制图表。
主要特点和功能:
- 统计图表: 提供了针对统计分析常用的图表类型,如箱线图、小提琴图、热图、聚类图等。
- 内置主题和调色板: 具有美观的默认主题和调色板,使得图表的外观更加吸引人。
- 数据探索和分析: 支持对数据集的直观探索,可用于探索数据的分布、关系等。
- 与Pandas集成: 能够方便地与Pandas等库结合使用,直接绘制DataFrame中的数据。
- 多变量图表: 支持绘制多变量之间的关系图、热图等复杂图表。
用途和应用场景:
- 数据探索和分析: 在数据科学领域中广泛应用,用于数据探索、可视化数据分布、关系等。
- 统计分析报告: 用于生成漂亮的图表,加入报告和论文中,提供直观的数据支持。
- 数据可视化: 作为Matplotlib的补充,提供更高级、更美观的图表,适用于各种数据可视化需求。
基本用法示例:
绘制箱线图:
xxxxxxxxxximport seaborn as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 加载示例数据集tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips)plt.xlabel('日期')plt.ylabel('账单')plt.title('每日总账单方框图')# Windows 设置显示中文plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'plt.show()

- 绘制小提琴图:
xxxxxxxxxximport seaborn as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载示例数据集tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips)plt.xlabel('日期')plt.ylabel('账单')plt.title('每日总账单小提琴图图')# Windows 设置显示中文plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'plt.show()
- 绘制热图:
xxxxxxxxxximport seaborn as snsimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 创建一个矩阵数据data = sns.load_dataset("flights").pivot("month", "year", "passengers")
sns.heatmap(data, annot=True, fmt="d", cmap="YlGnBu")plt.xlabel('年')plt.ylabel('月')plt.title('航班乘客热呈图')plt.show()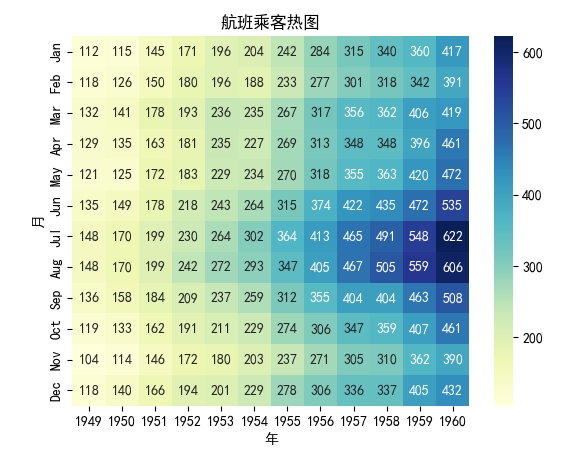
4-2. scikit-learn
scikit-learn(sklearn)是一个用于机器学习和数据挖掘的Python库,提供了各种机器学习算法实现和简单而有效的工具,用于数据挖掘和数据分析。它建立在NumPy、SciPy和Matplotlib之上,包含了各种机器学习算法和工具,适用于各种机器学习任务。
- 主要特点和功能
- 丰富的机器学习算法: 包含了许多常用的监督学习和无监督学习算法,如回归、分类、聚类、降维等。
- 易于使用的API: 具有统一和一致的API,使得用户可以方便地实现各种机器学习算法。
- 数据预处理和特征工程: 提供了数据预处理、特征选择、特征提取等功能,用于准备数据以供模型训练。
- 模型评估和验证: 提供了各种评估指标和验证方法,用于评估模型的性能和泛化能力。
- 与其他库的集成: 可以与NumPy、Pandas等库无缝集成,方便处理和转换数据。
- 可扩展性和灵活性: 支持模型的扩展和自定义,用户可以方便地实现自定义的机器学习算法。
常见的机器学习任务
- 分类: 区分数据点属于哪个类别,如垃圾邮件分类、图像识别等。
- 回归: 预测数值型数据,如房价预测、股票价格预测等。
- 聚类: 将数据分成不同的组别,发现数据中的模式,如用户分群、市场细分等。
- 降维: 减少数据集维度,保留主要特征,如图像处理、文本挖掘等。
基本用法示例
- 简单的线性回归示例
xxxxxxxxxxfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom sklearn.datasets import make_regressionfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errorimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体以支持中文显示plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 生成随机回归数据集X, y = make_regression(n_samples=100, n_features=1, noise=20, random_state=42)
# 划分数据集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 创建线性回归模型并拟合数据model = LinearRegression()model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测并评估模型y_pred = model.predict(X_test)mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)print("均方误差:", mse)
# 可视化结果plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='black')plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='blue', linewidth=3)plt.xlabel('X')plt.ylabel('y')plt.title('线性回归')plt.show()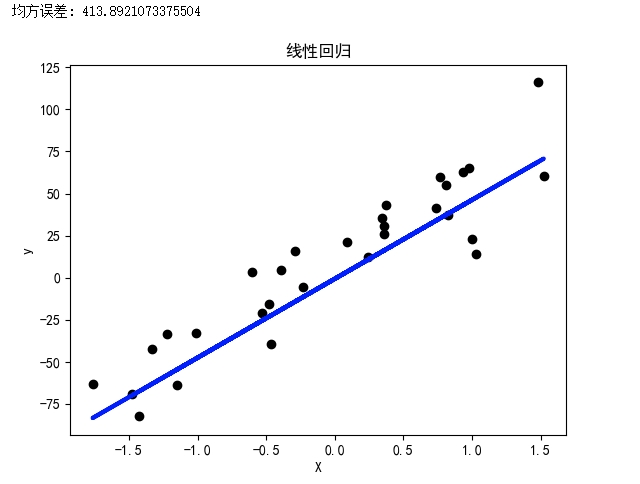
- K-Means聚类示例
xxxxxxxxxxfrom sklearn.datasets import make_blobsfrom sklearn.cluster import KMeansimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体以支持中文显示plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 生成随机聚类数据X, _ = make_blobs(n_samples=300, centers=4, cluster_std=0.60, random_state=42)
# 构建并拟合K-Means模型kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=4)kmeans.fit(X)
# 可视化聚类结果plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=kmeans.labels_, cmap='viridis')plt.scatter(kmeans.cluster_centers_[:, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[:, 1], s=300, c='red', marker='*', label='聚类中心')plt.title('K-Means聚类')plt.legend()plt.show()
- 决策树分类示例
xxxxxxxxxxfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scorefrom sklearn.tree import plot_tree
# 设置中文字体以支持中文显示plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 加载鸢尾花数据集iris = load_iris()X, y = iris.data, iris.target
# 划分数据集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# 构建并拟合决策树模型clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3, random_state=42)clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测并评估模型y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)print("准确率:", accuracy)
# 可视化决策树plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))plot_tree(clf, feature_names=iris.feature_names, class_names=iris.target_names, filled=True)plt.show()
- 工商企业预测年营业额示例
假设我们想要根据企业的注册资本、成立年份、行业等信息来预测企业的年营业额。以下是一个简化的示例
xxxxxxxxxximport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errorimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as np
# 设置中文字体以支持中文显示plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 手动生成示例数据(假设这是一个简化的数据集)np.random.seed(42)data = { '注册资本': np.random.randint(100, 1000, 50), '成立年份': np.random.randint(2000, 2020, 50), '行业': np.random.choice(['制造业', '服务业', '零售业'], 50), '年营业额': np.random.randint(100000, 1000000, 50)}
# 创建DataFramedf = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 对行业进行独热编码df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=['行业'])
# 数据预处理,选择特征和目标值X = df[['注册资本', '成立年份', '行业_制造业', '行业_服务业', '行业_零售业']]y = df['年营业额']
# 划分数据集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建线性回归模型并拟合数据model = LinearRegression()model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测并评估模型y_pred = model.predict(X_test)mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)print("均方误差:", mse)
# 可视化结果(展示预测值和实际值的对比)plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))plt.plot(range(len(y_pred)), y_pred, label='预测年营业额', marker='o')plt.plot(range(len(y_test)), y_test, label='实际年营业额', marker='x')plt.xlabel('样本编号')plt.ylabel('年营业额')plt.title('年营业额预测结果')plt.legend()plt.show()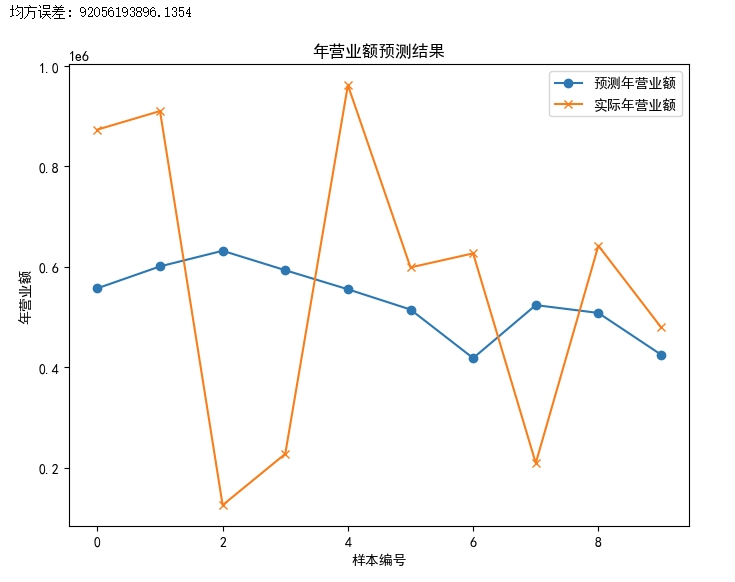
4-3. Keras
Keras 是一个高层神经网络 API,它可以运行在 TensorFlow、Theano 和 Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit(CNTK)之上,使得深度学习任务更加简单和快速。它设计用来快速试验和搭建神经网络模型,具有易用性和灵活性。
- 主要特点和功能
- 用户友好性: Keras 提供了简洁一致的 API,易于使用和理解,适合初学者和专业人士。
- 模块化和可组合性: 允许用户通过堆叠层的方式快速构建神经网络模型,模块化程度高,便于修改和扩展。
- 支持多种神经网络类型: 支持多种类型的神经网络,包括卷积神经网络(CNN)、循环神经网络(RNN)、深度强化学习等。
- 灵活性: 可以在 CPU 和 GPU 上无缝运行,支持快速实验和迁移学习。
- 易于扩展: 可以通过添加自定义层、损失函数、激活函数等来定制模型。
- 内置高级功能: 提供了各种内置功能,如图像处理、序列处理、优化器、损失函数等。
- 广泛的社区支持: 拥有庞大的用户社区和开发者支持,提供了丰富的文档和示例。
- Keras 的基本用法示例
以下是一个简单的示例,展示了如何使用 Keras 来构建一个简单的全连接神经网络,并训练一个分类模型:
xxxxxxxxxximport kerasfrom keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import Densefrom keras.optimizers import Adamfrom sklearn.datasets import make_classificationfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 生成分类数据X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_classes=2, random_state=42)
# 划分数据集X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建模型model = Sequential()model.add(Dense(64, input_shape=(20,), activation='relu'))model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu'))model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
# 编译模型model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.001), loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=10, validation_data=(X_test, y_test))
# 可视化训练过程import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='训练准确率')plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label='验证准确率')plt.xlabel('Epochs')plt.ylabel('准确率')plt.legend()plt.show()
/**Epoch 1/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 6ms/step - loss: 0.6231 - accuracy: 0.6900 - val_loss: 0.5630 - val_accuracy: 0.7400Epoch 2/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4710 - accuracy: 0.8525 - val_loss: 0.4817 - val_accuracy: 0.7850Epoch 3/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3752 - accuracy: 0.8763 - val_loss: 0.4277 - val_accuracy: 0.8150Epoch 4/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3247 - accuracy: 0.8925 - val_loss: 0.4103 - val_accuracy: 0.8300Epoch 5/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2992 - accuracy: 0.8950 - val_loss: 0.4085 - val_accuracy: 0.8300Epoch 6/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2821 - accuracy: 0.9025 - val_loss: 0.4048 - val_accuracy: 0.8400Epoch 7/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2696 - accuracy: 0.9038 - val_loss: 0.3964 - val_accuracy: 0.8400Epoch 8/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2598 - accuracy: 0.9025 - val_loss: 0.4061 - val_accuracy: 0.8400Epoch 9/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2484 - accuracy: 0.9150 - val_loss: 0.4035 - val_accuracy: 0.8350Epoch 10/1025/25 [====================] - 0s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2383 - accuracy: 0.9125 - val_loss: 0.4063 - val_accuracy: 0.8550**/